
History of Odisha Intro
The history of Odisha, a state situated on the eastern coast of India, is a tapestry of ancient civilizations, dynastic rule, cultural efflorescence, and periods of foreign influence. Stretching back millennia, Odisha’s history is a testament to the resilience and creative spirit of its people. Here’s a more descriptive introduction to the history of Odisha:
Ancient Origins: Odisha’s history can be traced back to ancient times when it was known as Kalinga. Archeological evidence suggests human habitation in the region dating back to the Stone Age. The Mauryan Emperor Ashoka’s conquest of Kalinga in the 3rd century BCE is a defining moment in the state’s history, as it led to the spread of Buddhism and a lasting impact on the region’s culture.
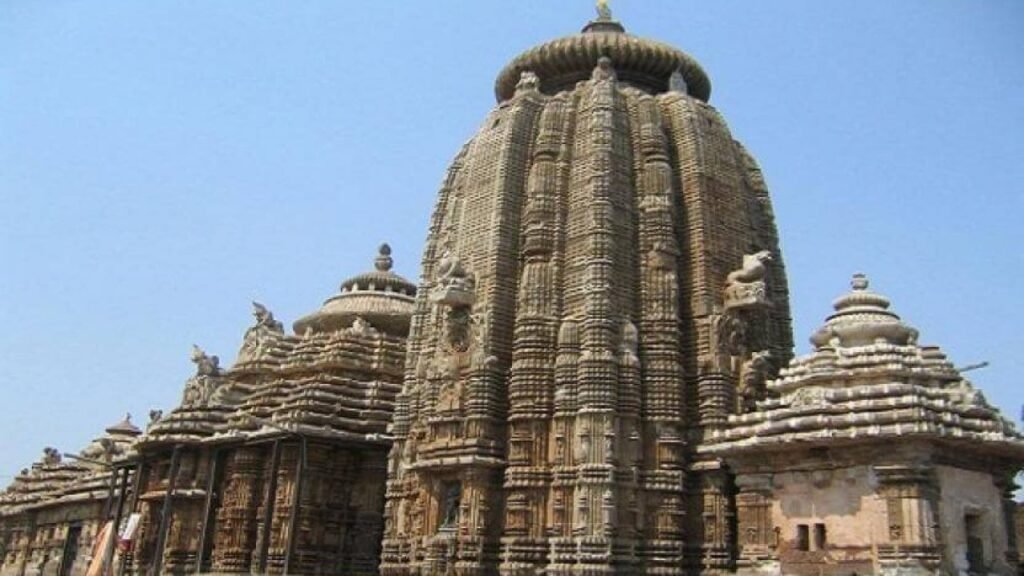
Golden Era of Dynasties: Odisha’s history is marked by the rise of several dynasties, including the Satavahanas, Guptas, and Matharas. The Gupta Emperor Samudragupta’s rule in the 4th century CE brought prominence to the region. However, it was during the rule of the Kalinga Dynasty that Odisha truly blossomed. Their patronage of art, architecture, and literature left an indelible mark on the state. The exquisite Konark Sun Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a prime example of their architectural prowess.
Ganga Dynasty and Eastern Ganga Dynasty: The Ganga Dynasty, reigning from the 11th to the 15th centuries CE, contributed significantly to Odisha’s cultural and historical legacy. The construction of magnificent temples, including the renowned Jagannath Temple in Puri, exemplifies their devotion to art and religion. Their successor, the Eastern Ganga Dynasty, continued this cultural flourishing, leaving a rich heritage of art and architecture.
Mughal and Maratha Influence: During the 16th century, the Mughals, led by Emperor Akbar, brought Odisha under their dominion, leading to a period of cultural amalgamation. The Marathas later assumed control in the 18th century, shaping the region’s political landscape.
Colonial Era and Independence: The British East India Company took control of Odisha in the 19th century, making it part of British India. However, the state played a crucial role in the Indian independence movement. On April 1, 1936, Odisha was established as a separate province. In 1947, India gained independence from British colonial rule, and Odisha became a full-fledged state within the Indian Union.
Modern Odisha: Post-independence, Odisha has evolved into a diverse and culturally vibrant state. It has made significant strides in various fields, including education, industry, and agriculture. The state is known for its beautiful temples, rich traditions, and a strong commitment to preserving its cultural heritage.
The history of Odisha is a captivating narrative of an ancient land that has witnessed the rise and fall of dynasties, cultural flourishing, and foreign influences, all of which have contributed to its unique identity and enduring legacy.
History of Odisha 8 facts
History of Odisha 8 facts
Odisha, a state located on the eastern coast of India, is rich and diverse, spanning several millennia. Here’s a brief overview of its history:
- Ancient Period (Prehistoric to 4th Century CE):
The region that is now Odisha has evidence of human habitation dating back to prehistoric times. It was an important center of maritime trade with the ancient civilizations of Southeast Asia and the Mediterranean. The Mauryan Emperor Ashoka’s rock edicts can be found in Dhauli, near the modern city of Bhubaneswar. - Golden Age of Kalinga (4th – 12th Century CE):
The Gupta dynasty had a significant influence on the region, and it flourished under various dynasties like the Kharavela of the Chedi dynasty and the Ganga dynasty. The famous Jagannath Temple in Puri was built during this period. Buddhism and Jainism were prominent religions during this era. - Medieval Period (13th – 16th Century CE):
The Gajapati dynasty ruled the region during this time and maintained a strong cultural connection with Southeast Asia. The Sun Temple at Konark, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, was built during this period. Odisha also had a thriving maritime trade and cultural exchange with countries like Indonesia and Cambodia. - Mughal and Maratha Rule (16th – 18th Century CE):
Odisha came under the control of the Mughal Empire during the 16th century. Later, the Marathas established their authority over the region. The British East India Company gradually extended its influence, leading to the Battle of Cuttack in 1803, which marked the beginning of British colonial rule in Odisha. - Colonial Era (19th – 20th Century CE):
Odisha was initially a part of the Bengal Presidency under British rule. It gained separate status in 1936 as a province of British India. The struggle for independence gained momentum in Odisha, with leaders like Utkal Gourav Madhusudan Das and Biju Patnaik playing pivotal roles.
also readA deep dive : festival of odisha - Post-Independence Period (1947 – Present):
Odisha became a part of the Indian Union after India gained independence in 1947. The state has made significant progress in various sectors, including education, agriculture, industry, and infrastructure. It’s known for its natural resources, vibrant culture, and traditional arts and crafts. - Natural Disasters and Challenges:
Odisha has also faced its share of challenges, including devastating cyclones such as the 1999 Odisha cyclone. The state has undertaken efforts to improve disaster management and resilience. - Cultural Heritage:
Odisha boasts a rich cultural heritage, with various dance forms like Odissi and folk dances, intricate handicrafts, and a unique culinary tradition. The state’s festivals like Rath Yatra in Puri and Durga Puja are celebrated with great enthusiasm.
Overall, the history of Odisha is characterized by its maritime trade, architectural marvels, dynastic rule, and cultural vibrancy, making it a significant and diverse part of India’s historical tapestry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the history of Odisha is a captivating journey through the ages, revealing the rich tapestry of this eastern Indian state’s past. From its ancient origins as Kalinga, Odisha has been a land of cultural splendor and historical significance.
Throughout its history, Odisha has seen the rise and fall of dynasties, from the Mauryas and Guptas to the Kalinga and Ganga Dynasties. These rulers left behind a legacy of art, architecture, and literature, with magnificent temples and monuments that continue to inspire awe.
Foreign influences, including the Mughals and the Marathas, have added layers of complexity to Odisha’s history, shaping its cultural fabric. The region played a vital role in India’s struggle for independence, ultimately achieving statehood in 1936.
Modern Odisha is a testament to its rich heritage, with a thriving culture that celebrates its past while embracing the future. The state’s commitment to preserving its traditions, its contributions to art, literature, and religion, and its ongoing development make it a unique and vibrant part of India’s diverse tapestry.
As Odisha continues to evolve, its history remains a source of inspiration and pride, a testament to the enduring spirit of its people, and a reminder of the cultural treasures that have been passed down through the ages.
FAQs
here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the history of Odisha along with brief answers:
- What is the history of Odisha?
- The history of Odisha is a rich tapestry that spans thousands of years. It includes ancient civilizations, dynastic rule, cultural flourishing, and periods of foreign influence.
- When did human habitation in Odisha begin?
- Archeological evidence suggests human habitation in Odisha dating back to the Stone Age, indicating a very ancient history.
- What is the significance of Emperor Ashoka in Odisha’s history?
- Emperor Ashoka’s conquest of Kalinga in the 3rd century BCE had a profound impact on the region, spreading Buddhism and influencing its culture.
- Which dynasties ruled over Odisha during its history?
- Odisha saw the rule of various dynasties, including the Mauryas, Guptas, Kalinga, Ganga, Eastern Ganga, and Marathas, each contributing to the state’s cultural and historical heritage.
- What are some notable architectural achievements in Odisha’s history?
- The Konark Sun Temple, Jagannath Temple in Puri, and various other exquisite temples and monuments built by different dynasties stand as remarkable architectural achievements.
- When did Odisha become part of British India, and when did it gain independence?
- Odisha came under British control in the 19th century. It became a separate province on April 1, 1936, and India gained independence in 1947.
- How has Odisha evolved in the modern era?
- Post-independence, Odisha has made significant progress in education, industry, and agriculture while preserving its cultural heritage and traditions.
- What is the cultural significance of Odisha today?
- Odisha is known for its vibrant culture, festivals, classical dance forms like Odissi, and a strong commitment to preserving its rich cultural heritage.
- Are there any UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Odisha?
- Yes, the Konark Sun Temple and the Jagannath Temple in Puri are among the UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Odisha.
- What role did Odisha play in India’s struggle for independence?
- Odisha played a crucial role in India’s independence movement, with notable leaders and movements contributing to the fight against British colonial rule.
These FAQs provide a glimpse into the multifaceted and historically significant journey of Odisha, a state with a deep and storied past.
also readThe wildlife of Odisha | A Natural Wonder













One thought on “History of Odisha | A brief overview”